お知らせ
-
界面水によるメタン活性化光触媒反応の促進効果に関する解説記事出版 (10/16)2023.10.16
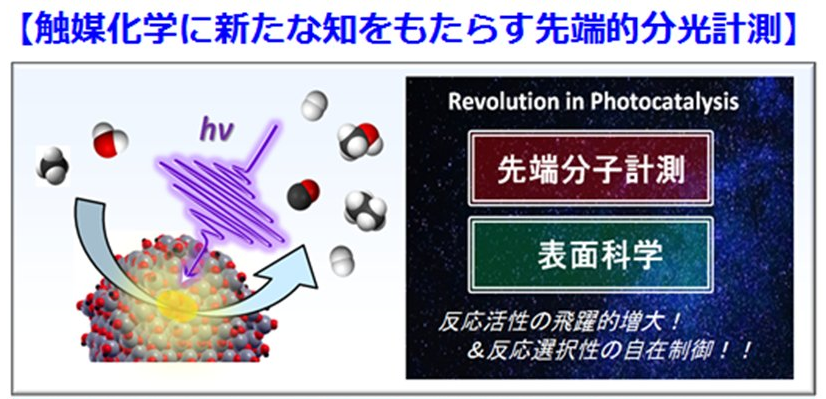
当グループの研究トピック5『水を酸化・還元剤とする極低環境負荷の革新的有機光合成』に関連して、界面水によるメタン活性化光触媒反応の促進効果に関する研究解説記事が出版されました。
研究内容ページ > 研究トピックへ
実触媒・実反応環境下の表面界面分子科学開拓への挑戦~界面水による光触媒的C-H活性化とメタン転換の促進効果~
杉本敏樹
表面と真空 , 66 巻 10 号, 580-586 (2023)
https://doi.org/10.1380/vss.66.580
室温・大気圧条件下でメタンを付加価値の高い化学物質に変換する次世代光触媒技術の開発は、持続可能社会の実現に向けて極めて重要な化学的課題である。しかしながら、メタンの反応メカニズムに関する微視的な知見がほとんど得られておらず、高機能なメタン転換光触媒の設計・開発指針が乏しいのが現状でした。本解説記事では、光触媒の表面反応場に水分子が存在することでメタンの転換効率や反応選択制が変化することを示した当グループの最近の研究結果を紹介しています。
Environmentally sustainable and selective conversion of methane to valuable chemicals under ambient conditions is pivotal for the development of next-generation photocatalytic technology. However, the lack of microscopic knowledge on its reaction mechanism prevents the development of engineering strategies for methane photocatalysis. Here we introduce key molecular-level insights into the photocatalytic green utilization of methane. Activation of the robust C–H bond of methane is hardly induced by the direct interaction with photogenerated holes trapped at the surface of photocatalyst ; instead, the C–H activation is significantly promoted by the photoactivated interfacial water species. The interfacial water hydrates and properly stabilizes hydrocarbon radical intermediates, thereby suppressing their overstabilization. Owing to these water-assisted effects, the photocatalytic conversion rates of methane under wet conditions are dramatically improved by typically more than 30 times at ambient temperatures (~300 K) and pressures (~1 atm) in comparison to those under dry conditions.
表面真空学会の会誌で解説記事が出版されました。https://t.co/qEq07Omm2d
実反応環境下の実触媒表面のオペランド分光計測・リアルタイム反応解析で明らかになってきた、界面水が本質的に作用するC-H活性化光触媒反応の促進現象について研究内容を紹介しています!
— 表面界面科学・先端分光研究室(杉本G)@分子科学研究所 (@SugimotoGroup) October 16, 2023